Community articles — Physics
Recent

Trabalho Prático 09 - Física Experimental Cefet/MG - Timóteo

Trabalho de Física Experimental II
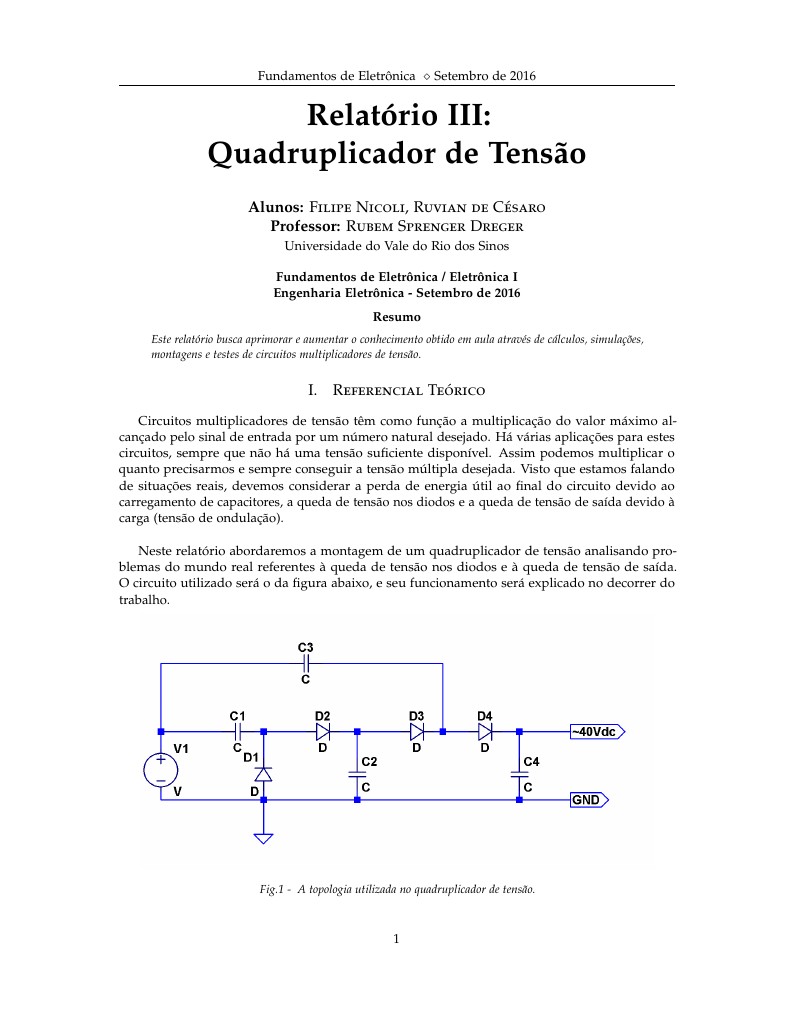
Este relatório busca aprimorar e aumentar o conhecimento obtido em aula através de cálculos, simulações, montagens e testes de circuitos multiplicadores de tensão.

This paper describes the three conditions of damped oscillations and the mathematical formulations of each condition.

Beamer theme "Cuerna", version 1.0 Copyright Gubertino Cavalieri (mathsguy@bluesimplex.com) October 2014. distributed under the GNU GPL Licence.

Sinds enkele jaren ben ik op zoek naar eenvoudige wiskundige en fysische problemen die onverwacht gerelateerd zijn met het getal \(\pi\). In The bouncing balls and pi beschreef ik eerder al hoe de opeenvolgende decimalen van \(\pi\) kunnen berekend worden door twee ballen volledig elastisch tegen elkaar en tegen een muur te laten botsen. In dit artikel zal ik aantonen hoe het getal \(\pi\) tevoorschijn komt door een oneindige serie rechthoeken met oppervlakte 1 spiraalsgewijze aan elkaar te kleven. In een veralgemening van dit probleem duikt op een natuurlijke wijze de gammafunctie en de formule van Stirling op.

Trabalho prático em Física Experimental II

The impact crater of a small metal ball of 63.7 grams (0.0637kg) is dropped from 8 different heights, ranging from 0.20m to 0.90m was observed. A mean was measured for the craters diameter. Using the equation E=mg$\Delta$h given that we have m, and g is a constant of 9.81 we can find the kinetic energy of the ball on impact. The relationship between crater diameter, D, and impact energy, E, is given by D=kE$^n$ where K is constant and n is found by the gradient of the graph and is also constant. This can be modified to give $\log D = n\log E + \log k$.

El barómetro es un instrumento de medición atmosérica, específicamente utilizado en la determinación de la fuerza por unidad de superficie ejercida por el peso de la atmósfera. Existe un gran número de equipos atmoféricos con distintos tipos de estos aparátos y son diariamente utilizados ya que la presión atmosférica juega un papel importante en la determinación y pronóstico del tiempo así como en el área de investigación al momento de realizarse experimentos ya que pueden llegar a afectar o hacer variar el funcionamiento de muchos aparatos electrónicos y mecánicos.
\begin
Discover why over 25 million people worldwide trust Overleaf with their work.